The TSP package (Hahsler and Hornik 2007) provides the basic infrastructure and some algorithms for the traveling salesman problems (symmetric, asymmetric and Euclidean TSPs). The package provides some fast implementations of simple algorithms including:
The package can read and write the TSPLIB format (Reinelt 1991) and it can solve many of the problems in the TSPLIB95 problem library (local copy of the archive).
The following R packages use TSP: archetypes, cholera, condvis, CRTspat, ForagingOrg,
ggEDA, isocir, jocre, MLCOPULA, nilde, nlnet, PairViz, pencopulaCond,
SCORPIUS, sensitivity,
seriation, sfnetworks, tspmeta, VineCopula
To cite package ‘TSP’ in publications use:
Hahsler M, Hornik K (2007). “TSP - Infrastructure for the traveling salesperson problem.” Journal of Statistical Software, 23(2), 1-21. ISSN 1548-7660, doi:10.18637/jss.v023.i02 https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v023.i02.
@Article{,
title = {TSP -- {I}nfrastructure for the traveling salesperson problem},
author = {Michael Hahsler and Kurt Hornik},
year = {2007},
journal = {Journal of Statistical Software},
volume = {23},
number = {2},
pages = {1--21},
doi = {10.18637/jss.v023.i02},
month = {December},
issn = {1548-7660},
}Stable CRAN version: Install from within R with
install.packages("TSP")Current development version: Install from r-universe.
install.packages("TSP",
repos = c("https://mhahsler.r-universe.dev",
"https://cloud.r-project.org/"))Load a data set with 312 cities (USA and Canada) and create a TSP object.
library("TSP")
data("USCA312")
tsp <- TSP(USCA312)
tsp## object of class 'TSP'
## 312 cities (distance 'euclidean')Find a tour using the default heuristic.
tour <- solve_TSP(tsp)
tour## object of class 'TOUR'
## result of method 'arbitrary_insertion+two_opt' for 312 cities
## tour length: 41941Show the first few cities in the tour.
head(tour, n = 10)## Winston-Salem, NC Charlotte, NC Asheville, NC Greenville, SC
## 306 54 10 110
## Spartanburg, NC Augusta, GA Columbia, SC Charleston, SC
## 260 14 64 52
## Savannah, GA Jacksonville, FL
## 250 127Visualize the complete tour.
library(maps)
data("USCA312_GPS")
plot((USCA312_GPS[, c("long", "lat")]), cex = 0.3)
map("world", col = "gray", add = TRUE)
polygon(USCA312_GPS[, c("long", "lat")][tour, ], border = "red")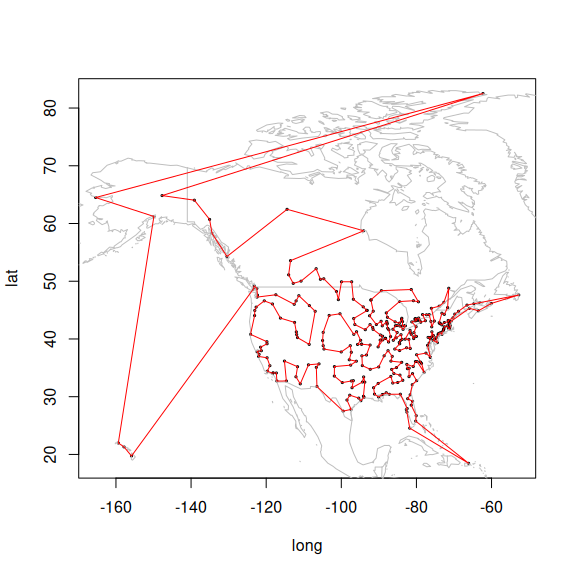
An online example application of TSP can be found on shinyapps.
You can find Q&A’s and ask your own questions at https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=TSP+R
Please submit bug reports to https://github.com/mhahsler/TSP/issues